Activation with low-pressure plasma
Individual modification or activation of surfaces
Bonding improvement on polymers
The surfaces of countless industry-relevant plastics such as polyolefins (PE, PP, EPDM or PTFE) are so nonpolar that they cannot be adequately wetted by paints, printing inks or adhesives. Bio-organic materials or metals are also often very difficult to coat or only with the aid of costly, specialized polymer products.
With low-pressure plasma technology it is possible to obtain an activation or chemical modification of polymer surfaces simply and efficiently. In numerous industrial applications, this process has already proven itself in terms of improved polymer processing properties (bonding, printing, painting, etc.).
Plasma activation – for excellent bonding properties in adhesive applications
In order to achieve adhesion between surfaces of nonpolar plastics and adhesives, lacquers, paints, etc., polar groups must be created on the surfaces. This results in an increase of the interfacial energies and therefore in an increase in affinity.
If this, in addition, results in formation of covalent chemical bonds between the substrate and the adhesive or coating, particularly good adhesion properties can be expected. Under such circumstances, the bond only breaks under high mechanical loads. It will not break at the interface but within the bonding components.
With low-pressure plasma technology, polar functional groups can be integrated into the surface of plastics. Depending on the gas applied, these may include oxygen groups such as –OH or nitrogen groups such as –NH2. This effect is limited to the surfaces themselves. The polymer bulk material is unaffected.
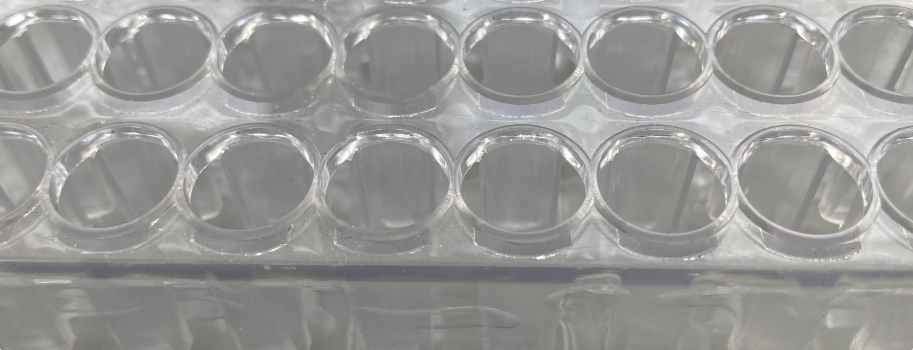
Plastic components

In medical technology, numerous plastic components are plasma treated in order to achieve improved hydrophilic properties on surfaces of microtiter plates, syringe hubs, etc.

Areas of application
- Automotive and automotive component industry
- Medical technology
- Electronic industry
- Electrical engineering
- Chip card production
- Plastics processing
- R & D
Example
Medical Technology: Needles
Steel needles have to be bonded to syringe hubs with high tensile strength to eliminate the risk of needle detachment during application. To achieve the desired bond strength, the polyethylene hubs are pretreated (activated) in plasma. Since plasma is gaseous, treating the interior of the hub is no problem.
Read more: Medical technology: Needles, PDF 196 KB More examplesHydrophobic polymer surface prior a treatment

A hydrophobic polymer surface prior a treatment with low-pressure plasma
After plasma treatment

The same surface has hydro-philic properties after plasma treatment
Bonding of the imprint

With the activation in low-pressure plasma, the surface tension increases and O-functional groups are incorporated into the PE surfaces
This improves bonding of the imprint
Long-term behavior of plasma-activated surfaces
Plasma activation produces covalent chemical bonds between oxygen and carbon atoms allowing interactions between the substrate's surface and the applied coating material because of their polarity. Such chemical bonds are stable over time and there is no degradation under normal storage conditions. However, storage stability is influenced by the following factors:
- Subsequent contamination from outside
- Subsequent contamination from inside
- Physical processes in the material
Physical deactivation
Directly after activation, all functional groups responsible for the activity are oriented towards the interface of the material. Over time, a statistic distribution of this orientation is achieved by means of rotations along the polymer chains around chemical single bonds. The groups are randomly oriented then and only a small part is available for interaction with the environment. Heat accelerates such processes because heat increases the mobility of the polymer chains.
ESCA analysis of a polypropylene surface
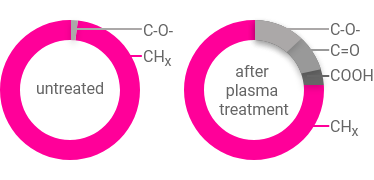
Composition of a plastic surface (PP) before and after oxygen plasma treatment
Storage effects
Activation at proper storage and handling may outlast several months especially in simple plastics without additives (like polypropylene). Proper storage means a storage preventing contamination from the outside at max. room temperature. However, a slight reduction of the surface tension always has to be expected but it is not necessarily relevant for the results.
In all other cases, a renewed cleaning / activation to revive the surface is normally non-critical. However, reliable statements only can be made after appropriate tests.
Contamination from outside
Subsequent contamination from outside may occur due to improper storage or handling: Contact with contaminated objects or hands, dirty atmosphere in the storage room, transfer of volatile material components of the packaging material.
Contamination from inside
Today, many plastics are optimized for special properties by additives: plasticizers, UV stabilizers, coloring agents, fire-resistant substances, and many others. Such additives often are not chemically bonded within the plastic matrix and are mobile within the material therefore. After activation, such straying small molucules cause a masking of the active surface. This might happen even very quickly.